Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree求二叉树的最小深度。
Example:
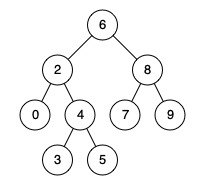
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
Output: 3
二叉树的深度可以通过深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索两种方式来遍历,并记录树的层次。
Solution
下面是Java的代码:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
return (left == 0 || right ==0) ? left + right + 1 : Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Deque<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
int depth = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()){
int size = q.size();
while (size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null){
return depth;
}
if (node.left != null){
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null){
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
|
下面是Python的代码:
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode):
if not root:
return 0
if not root.left and not root.right:
return 1
if root.left and not root.right:
return 1 + self.minDepth(root.left)
if root.right and not root.left:
return 1 + self.minDepth(root.right)
return 1 + min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right))
def minDepth(self, root):
if not root: return 0
q = collections.deque([(root, 1)])
while q:
curr, depth = q.popleft()
if not curr.left and not curr.right:
return depth
if curr.left:
q.append((curr.left, depth + 1))
if curr.right:
q.append((curr.right, depth + 1))
|
总结
第111题是简单题,只需熟悉二叉树的深度优先搜索与广度优先搜索,并记录对应的层次即可。
